A central challenge in the study of historical civilizations is the construction of evidence-based narratives describing complex processes of change that affected and shaped past societies. Archaeological evidence stems from multiple sources, such as excavations or complementary records on climate and other environmental factors. It is often fragmentary and has been subject to prior transformations, displacements, and preservation processes. Owing to the inherent difficulties of inferring the underlying spatio-temporal change processes from the data, their interpretation constitutes a prime subject for advanced mathematical modeling and formalized reasoning. Today, “agent-based models” (ABMs) are used to model processes involving human behaviour. This project aims to increase the explanatory power of ABMs in application to historical change processes including their validation and calibration against complex data. We are particularly interested in ABMs for innovation spreading processes in ancient cultures, incorporating geographic, climatic, and cultural aspects, community building and trading. Another focus is on efficient simulation of such models, in particular on high performance computing infrastructures.
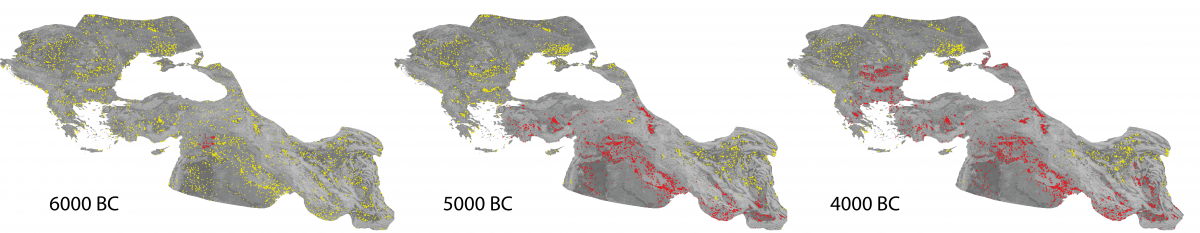
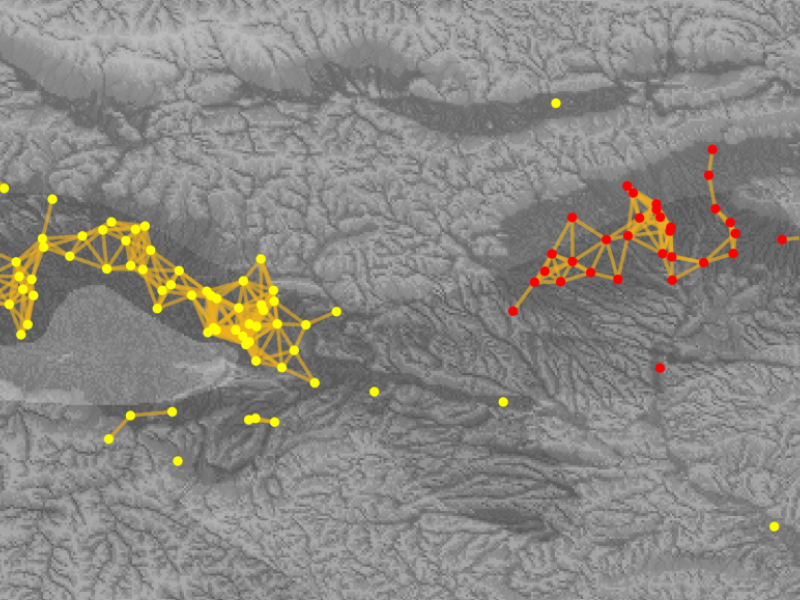
Figure 1: Snapshot of one realization of the wool-bearing sheep innovation spreading in ancient times.