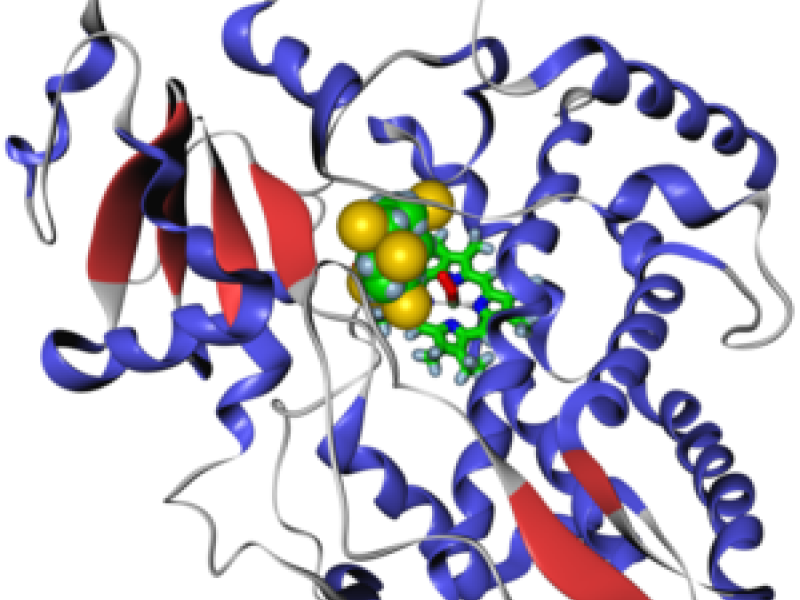
The cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are the major enzymes involved in drug metabolism and bioactivation. The most important reaction thereby is hydroxylation of CH groups, where the hydrogen is replaced by OH. We develop algorithms and software for predicting which CH groups of the substrate are attacked during the hydroxylation.