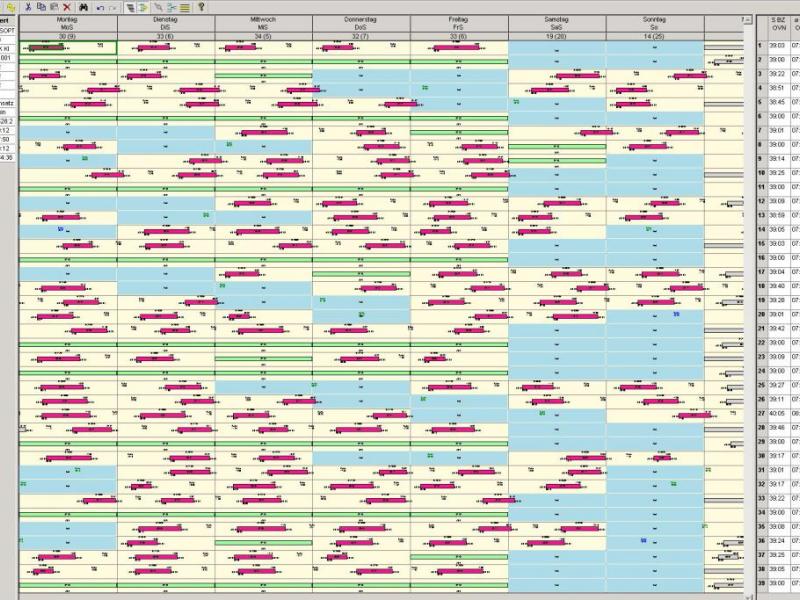
In the roster planning process duties must be brought to a lawful order. The arrangement of duties is based on very different rules. Here legal requirements, operational requirements, tariff requirements and other requirements are involved. One distinguishes between hard targets that must be respected and soft targets, that should be injured as little as possible. The more duties are considered, the more difficult it becomes to create a balanced and lawful weekly schedule by hand. As optimization goals it is considered mostly to minimize the rows, or to reach a uniform distribution of paid time. There are also other optimization goals conceivable. The aim of this project is to develop a weekly schedule optimization tool WS-OPT that solves these cyclic rostering problems.
Description
The next step in crew scheduling in public transport after duty scheduling is roster planning. To receive equitable roster schedules (weekly schedules), the duties are usually scheduled cyclically, so each employee is assigned the same duties over the entire period. The duties must not be freely combined.
The following types of roster planning rules are observed:
- Legal requirements
Some rules are fixed by law and must not be hurt. In Germany for example between two duties must be maintained a minimum distance of 9 hours. - Operational requirements
Within a company, there are agreements that go beyond legal requirements and also must not be violated. These requirements are in most cases results of collective agreements. - Other Requirements
In order to maximize employee satisfaction, there are guidelines that should be avoided if possible. This includes for example the uniform distribution of weekends with work. These requirements may be violated if it is not possible to comply with the operational and legal requirements otherwise.
Solution method
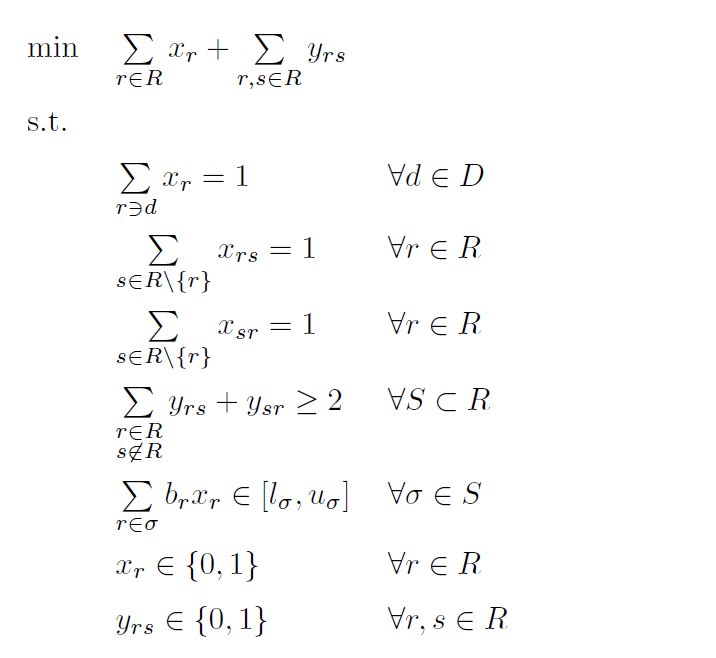
In our solution method, the cyclic rostering problem is modeled as a Set Partitioning problem and an acyclic Traveling Salesman problem. All duties must be assigned exactly to one row (Set Partitioning) and the rows need to be combined into one large cyclic weekly schedule (acyclic TSP). In addition, constraints are added for the legal and operational requirements. All soft targets are added to the objective function with penalty factors.
Results
The weekly schedule optimization tool WS-OPT is integrated into the planning system IVU.plan of IVU Traffic Technologies AG. Several projects with data from national and international public transport companies have shown that WS-OPT is able to generate better solutions than the solutions made by hand.