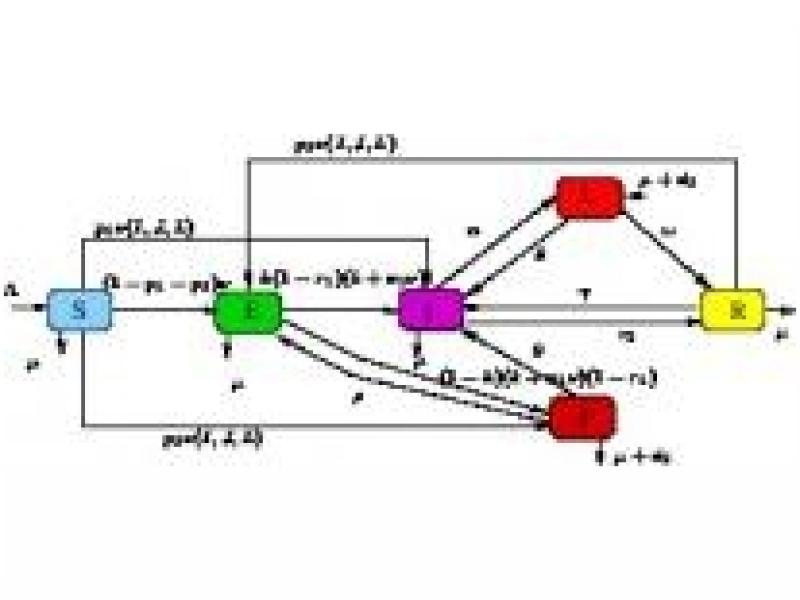
Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and curable disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) that most often affects the lungs. Mtb’s infection can remain latent, become active, or it can progress from latent TB to active TB either by endogenous re-activation and/or exogenous re-infection. Active TB is most of the time acquired through co-infection of Mtb with other diseases (diabetes, HIV/AIDS) or some substance abuse such as alcohol and tobacco.
The mathematical analysis of biomedical and disease transmission models can significantly contribute to the understanding of the mechanisms of those processes and to the design of potential therapies.