The interdisciplinary project Trassenbörse deals with the problem, wether an auction-based allocation of railway tracks could lead to competitive marketing of a railway infrastructure network. The idea is that competing railroad traffic companies can bid for any imaginable track. Possible arsising conflicts will be resolved by using the revenue maximizing allocation. In this project we investigate on the producibility and practicability of this approach. Together, we work on the occuring economic, railway environmental and mathematical problems.
TrassenbörseSlot Allocation for RailwaysThe interdisciplinary project Trassenbörse deals with the problem, wether an auction-based allocation of railway tracks could lead to competitive marketing of a railway infrastructure network. The idea is that competing railroad traffic companies can bid for any imaginable track. Possible arsising conflicts will be resolved by using the revenue maximizing allocation. In this project we investigate on the producibility and practicability of this approach. Together, we work on the occuring economic, railway environmental and mathematical problems. |  |
Goals
One great challenge is to model such a complex system like the railroad traffic, (especially the German one), in a convenient way. On the one hand it has to be possible to perform computational experiments based on that model, but on the other hand no important operating details must be ignored. Therefore our project partners from SFWBB and IVE work on two different approaches, whose combination should lead to this property. It is about a macroscopic railway model, which allows a rough planning through its simplified estimations(aggregation of input data). and a microscopic model, which permits a smooth simulation of runs of individual trains through its switch-level description. By adequate coupling of these models an iterative planning process should be realized from rough to smooth planning.
Another problem is to find a suitable design und rule set for auctioning such a complex manor like railway tracks and which leads to a more efficient use of railway capacity. Apart from this our project partner from WIP have been developing a flexible auction language, which achieves the requirements of an railway traffic company and gives him the possibility to specify their track requests; This is of great importance, mainly for practical reasons.
Problem
During an auction process, in each round a so called track allocation problem has to be solved to optimality on a macroscopic level. The solution corresponds to the allocated tracks and trains. First of all there is optimization potential by receiving more capacity through train bundling, see pictures below.
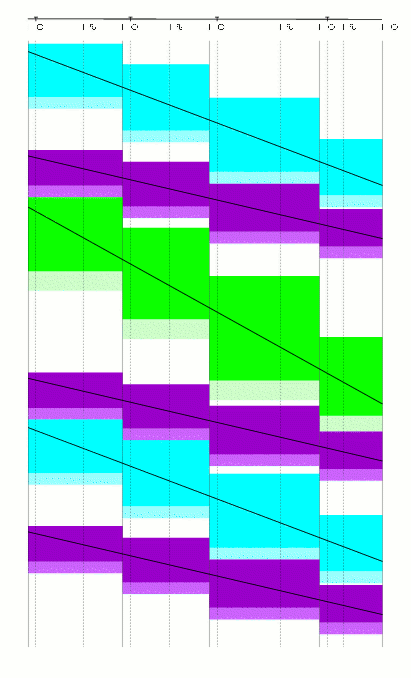 | 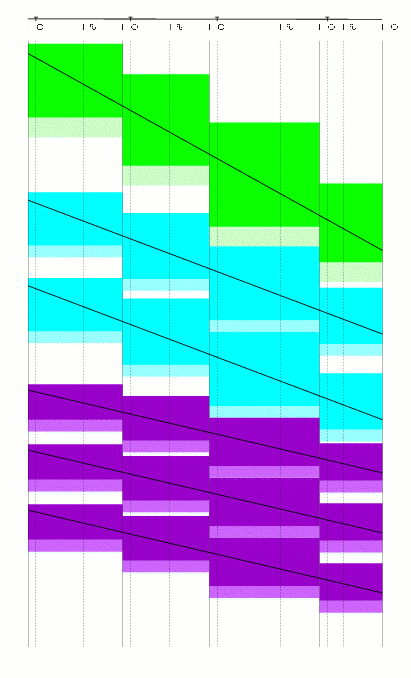 |
| Blocking times without bundling. | Blocking times with bundling. |
The determination of a train timetable or equivalent of a track allocation can be seen as one of the parade application examples for operations research. The right decision for the use of scare infrastructure capacity, that means the allocation on tracks and stations, has to be found. Obviously, this problem can be described in several ways. Therefore we worked on a standardization of the macroscopic timetabling problem -introducing TTPLib, see below.
Optimization
This combinatorial problem could be modelled as a multi commodity flow problem with additional packing constraints in a time expanded infrastructure digraph (see left figure below). Recent field of research are another model approach as coupled path covering problems. This is in some sense an extended model formulation of the arc packing problem formulation. We investigate on an integer programming approach to solve such problems by using the modeling language ZIMPL and the IP-Solver Software CPLEX. By using these tools we are able to solve scenarios with some hundreds of trains and a certain flexibility. To achieve our long-term goal, solving of large-scale and real-world scenarios, we have to improve the performance of our solution approach. Therefore we have started - at the current stage of the project - to develop an optimization tool, so called TS-OPT, that implements a special column generation algorithm for solving the coupled path covering model for the track allocation problem.
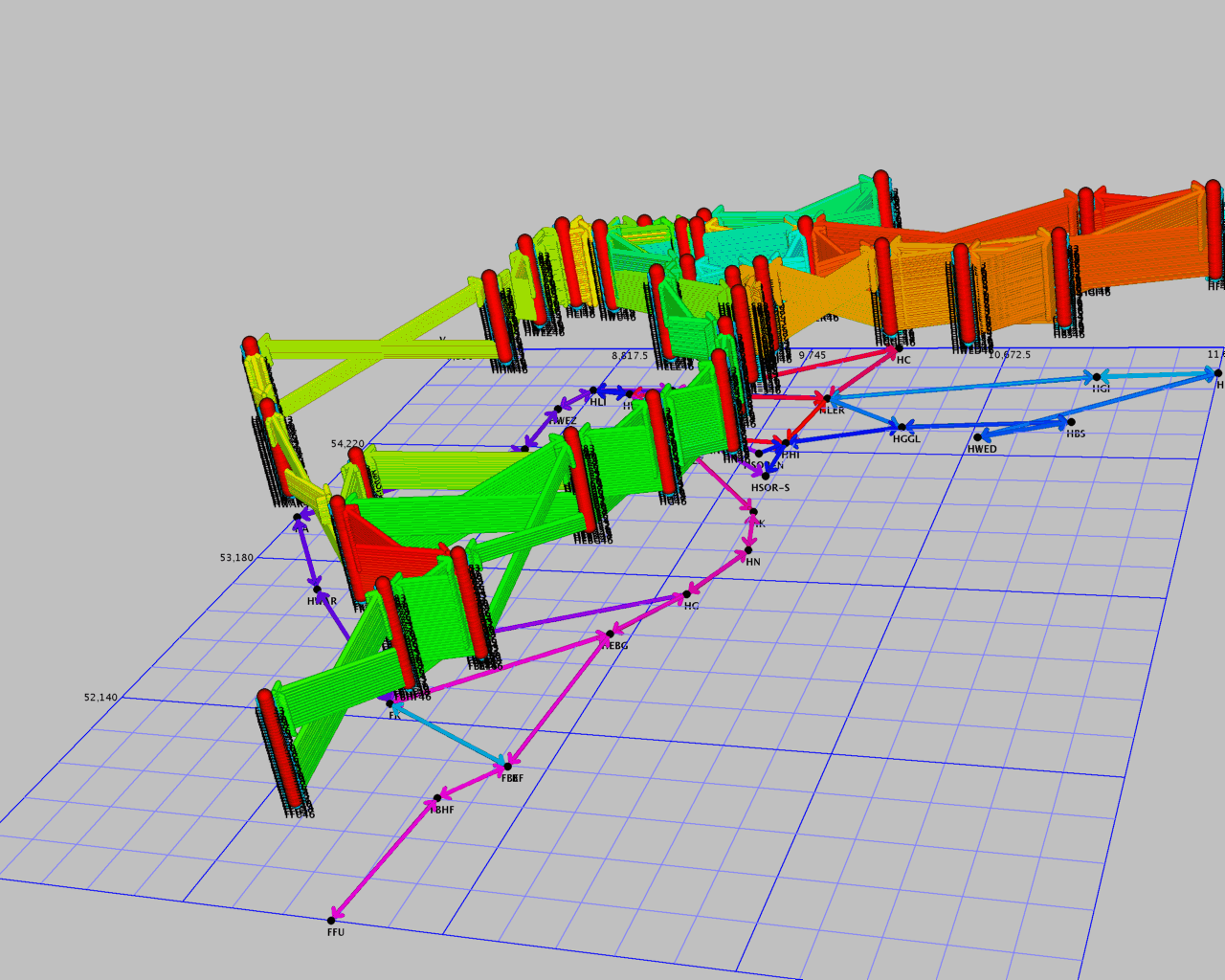 | 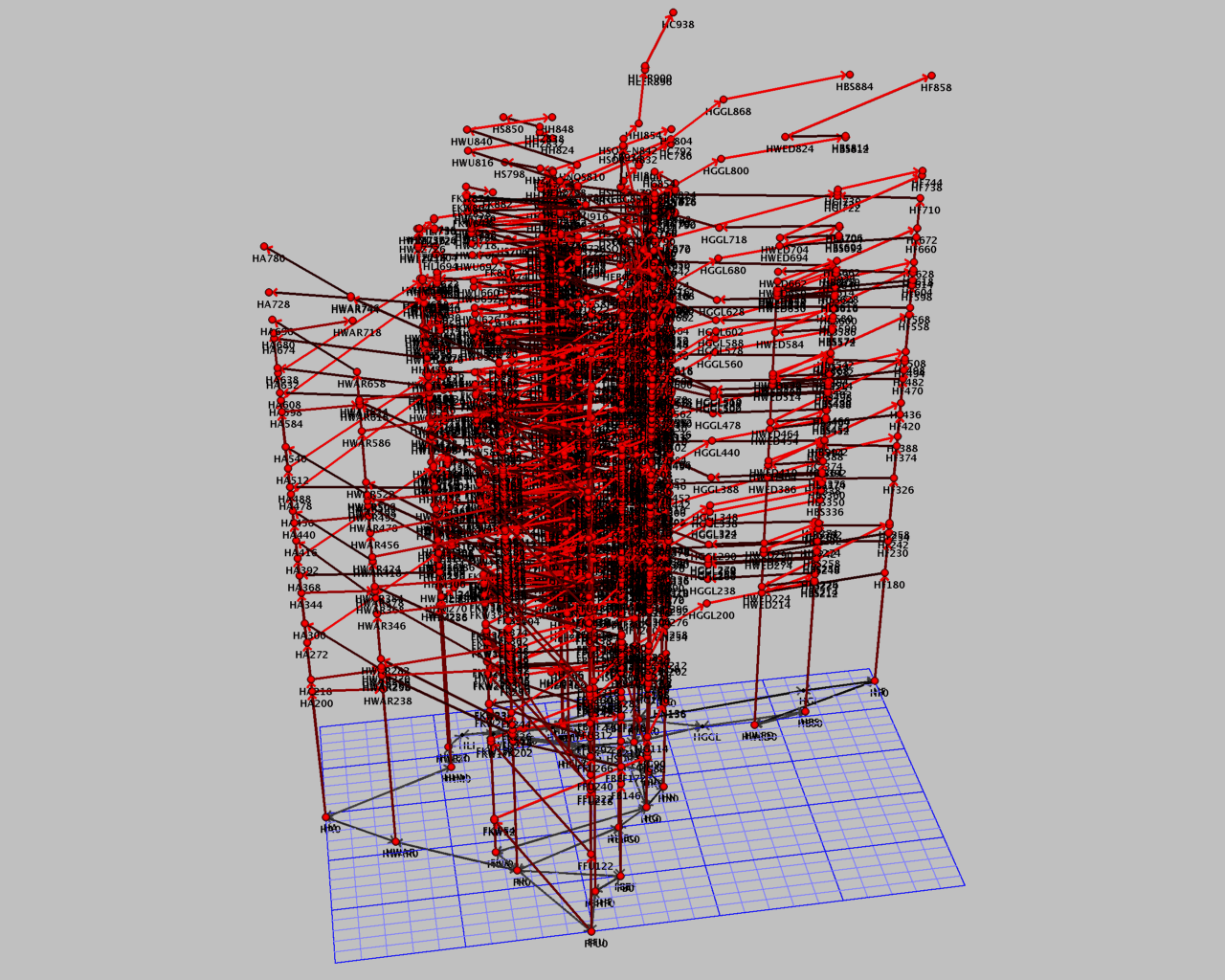 |
| Track-Scheduling-Graph. | Macroscopic Solution Schedule. |
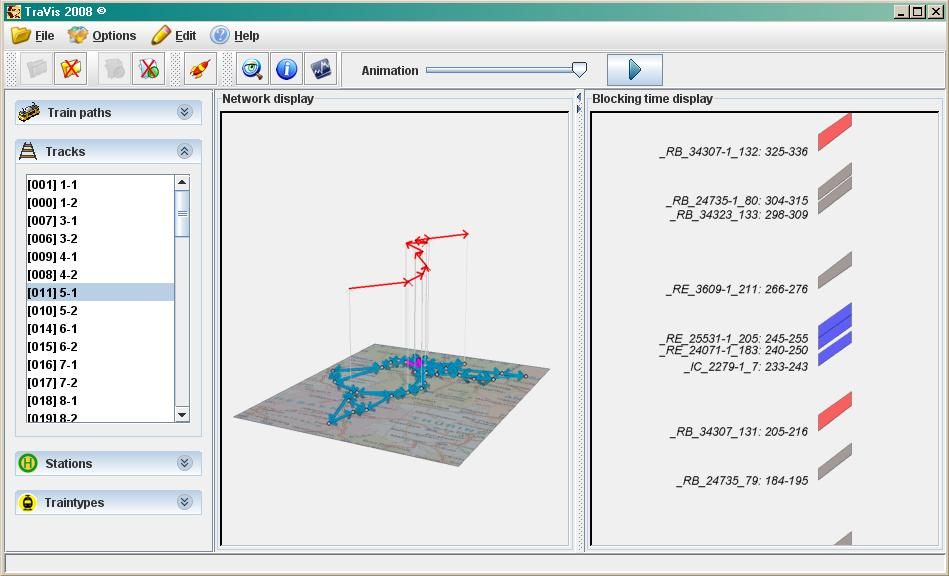
TraVis
Here is a link (> 8MB) to a live record of our visualization tool TraVis developed by M.Kinder and B.Erol based on JavaView. A feasible schedule for about 200 trains is animated. A free version for academic purposes can be downloaded here.
TTPLib
The Train Timetabling Problem Library TTPLib provides free access to our XML-specification of the problem, numerous instances and other useful information around the TTP.

Further Publications
- Anke Reuter. Kombinatorische Auktionen und ihre Anwendungen im Schienenverkehr. Master's Thesis, TU Berlin, 2005.
- Annette Mura. Trassenauktionen im Schienenverkehr. Master's Thesis, TU Berlin, 2006.
- Cemil Erdogan. Computing Prices for Track Allocations. Master's Thesis, TU Berlin, 2009.
- Berkan Erol. Models for the Train Timetabling Problem. Master's Thesis, TU Berlin, 2009.
