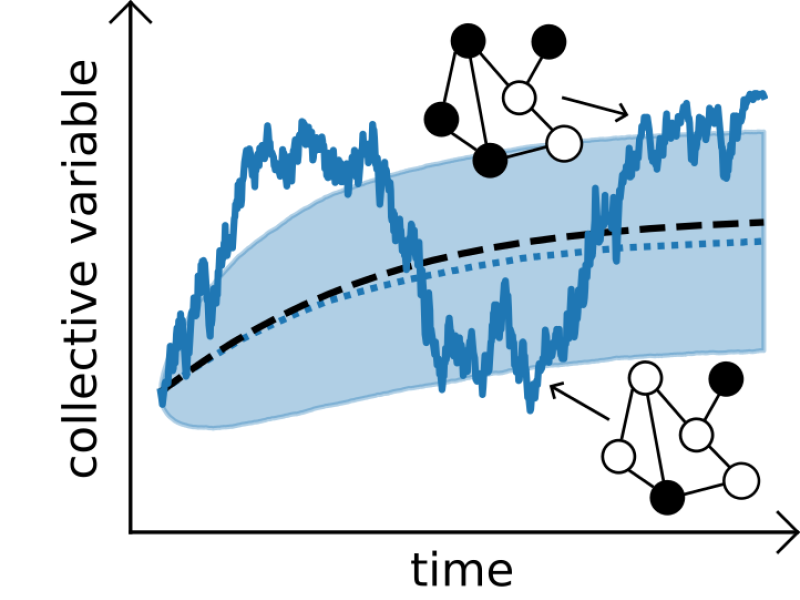
Analyzing dynamical systems on networks presents an important area of research that unveils a rich interplay between structure and dynamics, offering profound insights into the behavior of complex systems. The collective dynamics of interconnected components often lead to emergent phenomena that cannot be understood by examining individual entities in isolation. The study of dynamical systems on networks enables the exploration of these emergent behaviors, shedding light on how local interactions give rise to global patterns.
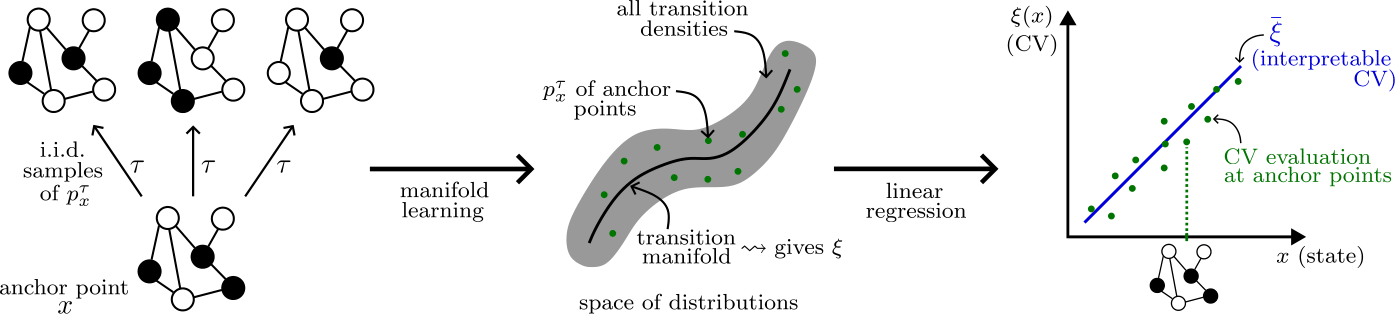
The transition manifold framework for network processes. Left: The random process is described by its distribution, sampled through a number of trajectories per initial network state (anchor). Middle: These distributions are used to learn a low-dimensional coordinate chart of the anchors. Right: A regression step allows for interpretability of the learned collective variable, yielding a function that can be evaluated in any state and not merely in anchor points.
The central goal of our project is to develop reduced models for spreading dynamics on networks, utilizing the constructive approach of collective variables. These models aim to faithfully reproduce the essential characteristics and emergent global phenomena of the original dynamics. Our specific objectives are:
- Interpretability: Matching physical intuition and collective variables.
- Practical forecast of collective variables' evolution.
- Use knowledge of collective variables and their evolution to capture regimes of socio-economic significance, such as epidemic threshold, network fragmentation, etc.
- Increase realism of the micro models by integrating temporal network evolution, non-Markovian dynamics, or inhomogeneities in the network structure.